How Recommendation Algorithms Work in Social Media

The social media recommendation system is by far the most mysterious yet rewarding secret. Anyone who understands algorithms captures trends and a large audience. Each social media have its own recommendation systems and its own specific, and the information on the Internet is very different.
To be the point developers themselves don't fully understand how their algorithms work.
One notable example of recent years is TikTok. Thanks to precise recommendation algorithms, the short video service managed not only to overtake all competitors but also to force them to copy this successful feature. We can say TikTok's algorithms have turned all social media content on its head.
What about statistics?
• Recommended products account for 35% of Amazon revenue. (McKinsey)
• On Netflix, 75% of video views are from recommendations (McKinsey).
• In a survey of 4,000 people, slightly more than half preferred an algorithm to a human when they thought a decision would be faster, cheaper, and more accurate (Bambauer & Risch, "Worse Than Human?" Arizona State Law Review 2021).
• In the US, researchers have documented that recommend systems clearly exposedright-wing extremist movements to users, as well as conspiracy theories regarding COVID-19 and the 2020 election results.
• As of 2019, the Instagram Explore recommendation engine retrieved 65 billion features and made 90 million model predictions per second.
• Clicking Dislike on YouTube, the most obvious way to leave a negative review, only stops 12% of bad recommendations (Mozilla).
• YouTube prioritizes watch time over user satisfaction (Mozilla).
Technical types of algorithms
Recommender systems can differ from each other and use different data. Before we analyze the recommendation systems of individual social networks, let's consider the technical types of algorithms when they are created.
Collaborative filtering
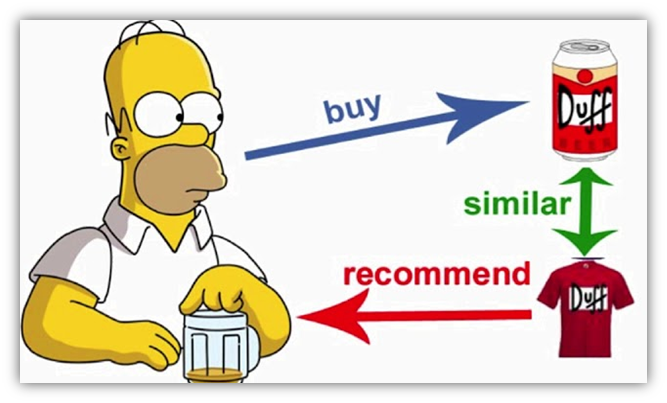
The collaboration system means if users previously had similar interests, then in the future, their interests probably will be similar.
User-based
The scheme is simple: two users A and B have similar preferences in music and artists. If user A likes a song that B has not yet heard, most likely listener B will like it too.
This principle is based on statistics about user preferences.
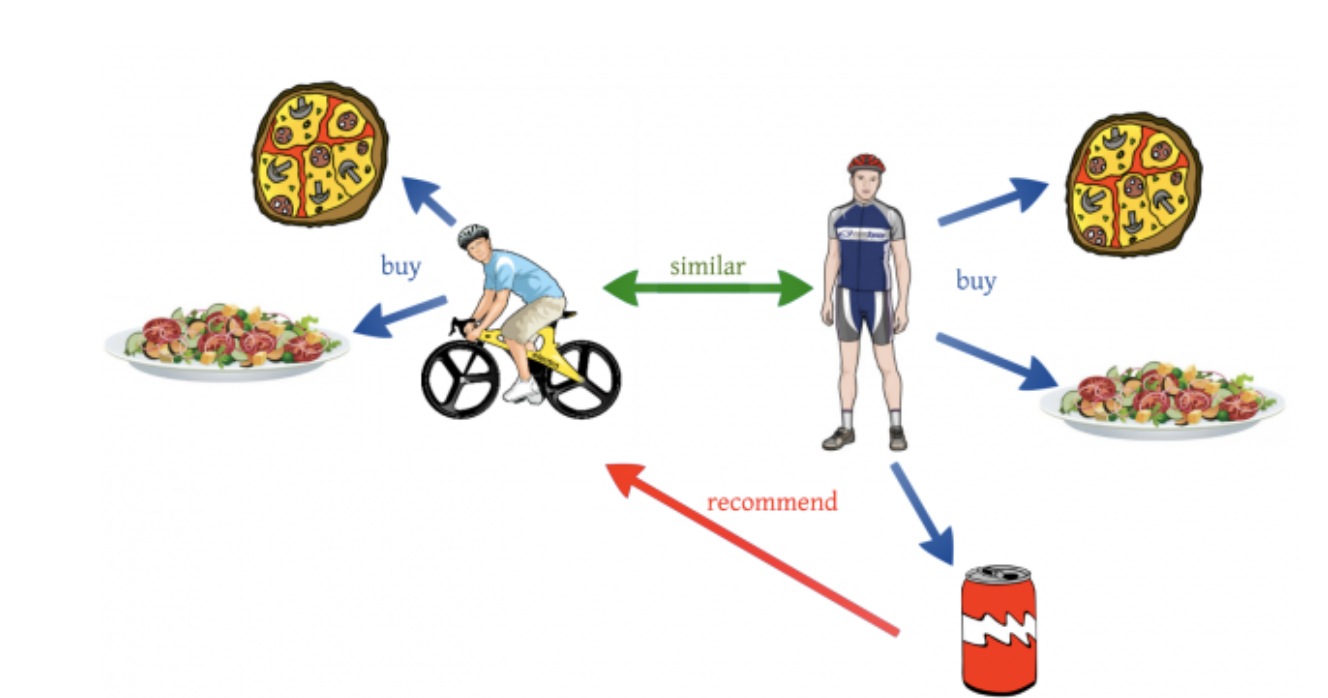
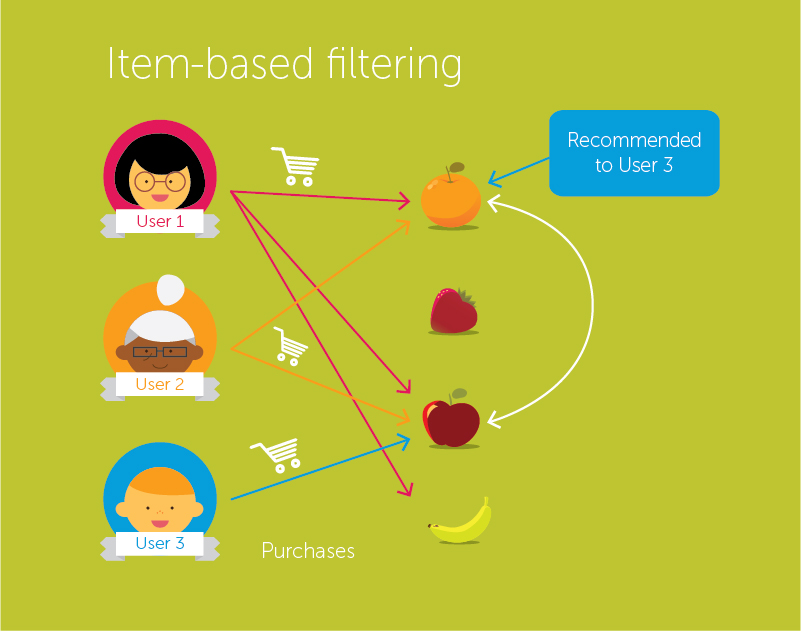
Item-based
A similar principle from among Collaborative filtering. In this case, the principle is not based on user preferences, but on the similarity of the object itself.
For example, users usually listen to songs A and B. If a person likes song A, then the system invited to listen to song B.
Recently, such an algorithm was directly shown by the VK Music service. The algorithm shows musical compatibility with other users and selects playlists based on matching tastes. In addition, you can find out what kind of music celebrities listen to and how compatible your musical tastes are.
Content-based
This principle creates "virtual portfolio" for each user, which considers the characteristics of the separate content elements (style, year, author, and so forth).
"Portfolio" is created basing on the user's preferences, or asked directly.
For example, a person prefers punk-rock and heavy metal from certain musicians, so similar styles and authors will be recommended to him.
Many bulletin boards work this way. A good example is the Craigslist or OLX, which offers similar ads, providing an opportunity to clarify the specific desires of the user.
Knowledge-based
Principle is usually used in areas where purchases are not made often (cars, apartments, expensive equipment). The system cannot build on the history of purchases, so it collects data at the very beginning.
For example, a person wants to buy a TV. We usually buy a TV every few years. If the system recommends TVs based on the preferences of other users, there are two risks: the match may not be correct and it will promote only bestsellers. Therefore, the algorithm tries to collect additional knowledge about the product and the user: price filtering, dimensions of interest, color, brand, and so forth.
Hybrid system
Recommender systems come in various types, but that doesn't mean should use just one. There are hybrid systems in which the above algorithms can be combined and complement each other.
An example is TikTok. When you register a new account, TikTok prompts you to select topics of interest and accounts of popular bloggers. After that, TikTok will show the most popular videos on the selected topics, and then it will consider your interests, interaction with content, the "Not interested" button, similarity of interests with other users, and so forth.
When creating a new account, the content will be determined separately, regardless of which device you are logged in from. Thus, you can create several accounts with different algorithm settings: sports, dancing, humor, etc.
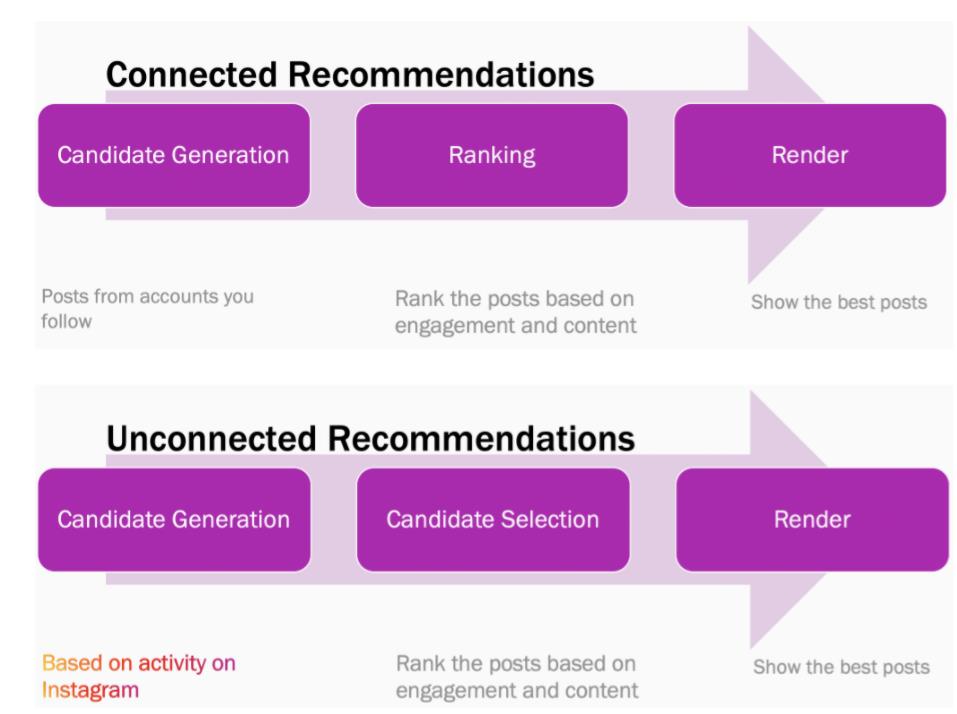
How the Instagram recommendation system works
Instagram algorithms work when:
A) The user scrolls the post feed
B) Instagram Explore (second tab from the bottom)
C) In Reels
Instagram also uses a recommend system to suggest more accounts to follow.
Feed post
Suggested posts you see on Instagram are recommended based on your and author activity:
1. What accounts do you follow and what posts do you interact with;
2. The titles of the posts you interact with;
3. How other users with similar interests interact with publications;
4. Publication date;
5. Your favorites;
6. Publication popularity;
7. How often have you interacted with a person's account over the past few weeks (the same principle is used to select the order in which Stories are displayed).
Instagram Explore
Getting featured on Instagram Explore is the same as getting your video featured in Reels. You will get a lot of outside audience attention. In general, not only posts end up in Explore but also Reels and even Stories.
Over 200 million accounts visit the Instagram Explore page daily. This is 50% of platform users. The Instagram algorithm ranks content based on several factors. These factors include engagement, freshness, content quality, and relevance.
The Explore recommendation system is like the posts feed, but differs in content from accounts that the user is not following gets here.
Reels
Reels is an undeniably great tool to promote your account. The algorithm is like Explore, Stories, and Feed, but as in other cases, Reels has its own.
Ranking factors:
User activity. Instagram keeps track of the videos people have interacted with. If a user interacts with your video, it signals to the algorithm to see more related content (including videos not by you).
2. User history. If the user continues to interact with your videos, the algorithm understands that your content interests him.
3. Information about the video. These include signals in the video, including music, sound effects, video understanding based on pixels and frames, and so forth. If you download a video from TikTok and upload it to Reels along with watermarks, the algorithm will immediately see it.
4. Information about the author's profile. Same with the post feed. The more a person interacts with your account, the more likely they are to see your new video.
Tip: When you post Reels, don't check the "Don't post to profile". Upload the video so that it appears on your profile. And if you don't like the profile view, then open the post, click the three dots in the upper right corner and "Remove from the profile". Thus, Reels will not appear on your profile, but it will get into the posts feed for followers. Otherwise, the video will only be displayed in the Reels tab.
TikTok recommendation system
We can talk endlessly about TikTok algorithms. This is something unknown and secret, and all the giants want to get their hands on it, so they make their own. Reminds me of the Krabby Patty recipe from SpongeBob.
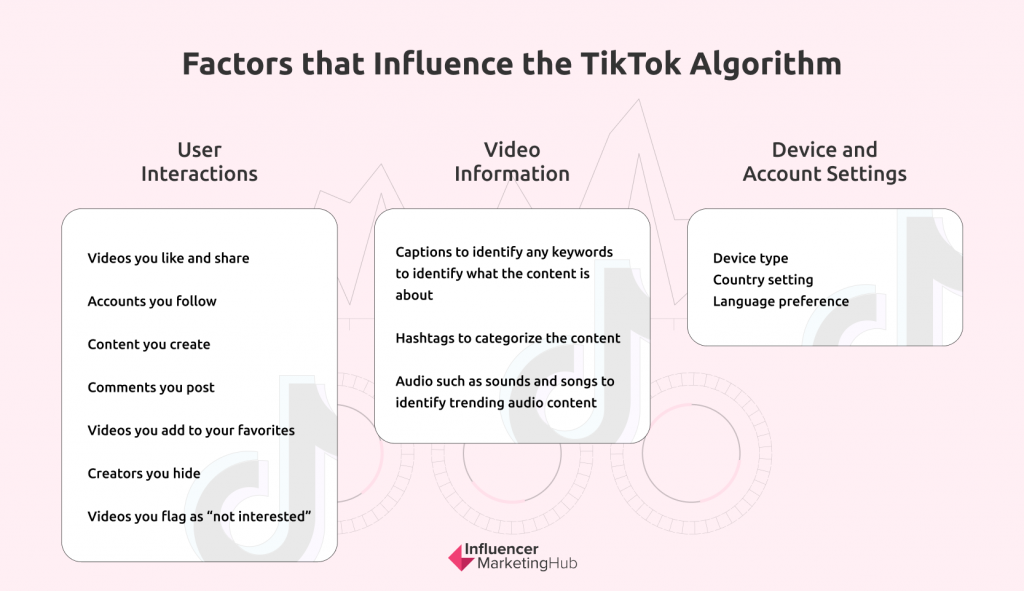
We cannot tell about all the pitfalls, but we will emphasize the fundamental principles. According to the official TikTok guide, the algorithm considers several factors before showing you a specific video on a specific topic:
They differ little from other social media and have a common principle: the algorithm adapts to the interests of the user. Key factors:
- Videos you like
Videos you share
Accounts you follow
Content you create
Comments you post
Videos you add to favorites
Authors you hide
Videos you mark as "uninteresting"
Also, the TikTok algorithm reads the information in some detail:
- Description of the video to identify any keywords that tell the algorithm what the content is about (works especially well when searching for a specific video).
- Hashtags to classify content and/or tell the algorithm what the video is about.
- Audio, such as sounds and songs, to identify trending audio content and provide it to a wider audience.
And TikTok considers the settings of your phone and SIM card:
- Device type
Country setting
Language Preference
The nuances of the algorithm:
After the video is published, it goes through pre-moderation, which can take from several minutes to several hours. In some cases, this is automatic moderation through a robot, if the account can be trusted, and sometimes it's manual. After pre-moderation, the video appears in the feed.
The algorithm tries to figure out the category of your video based on the factors above and user feedback.
The video appears randomly in the feed of followers, and show people from different categories. For example, the video will be in the feed of 20 followers (if any), and 20 people from different categories (for example, 4 car enthusiasts, 4 humor, 4 politics, etc.). If a certain category of video becomes interesting, and not only likes are considered but also the duration of viewing, shares, saves, copying links, pauses, etc., then TikTok increases the number of people to whom this video is displayed in this category.
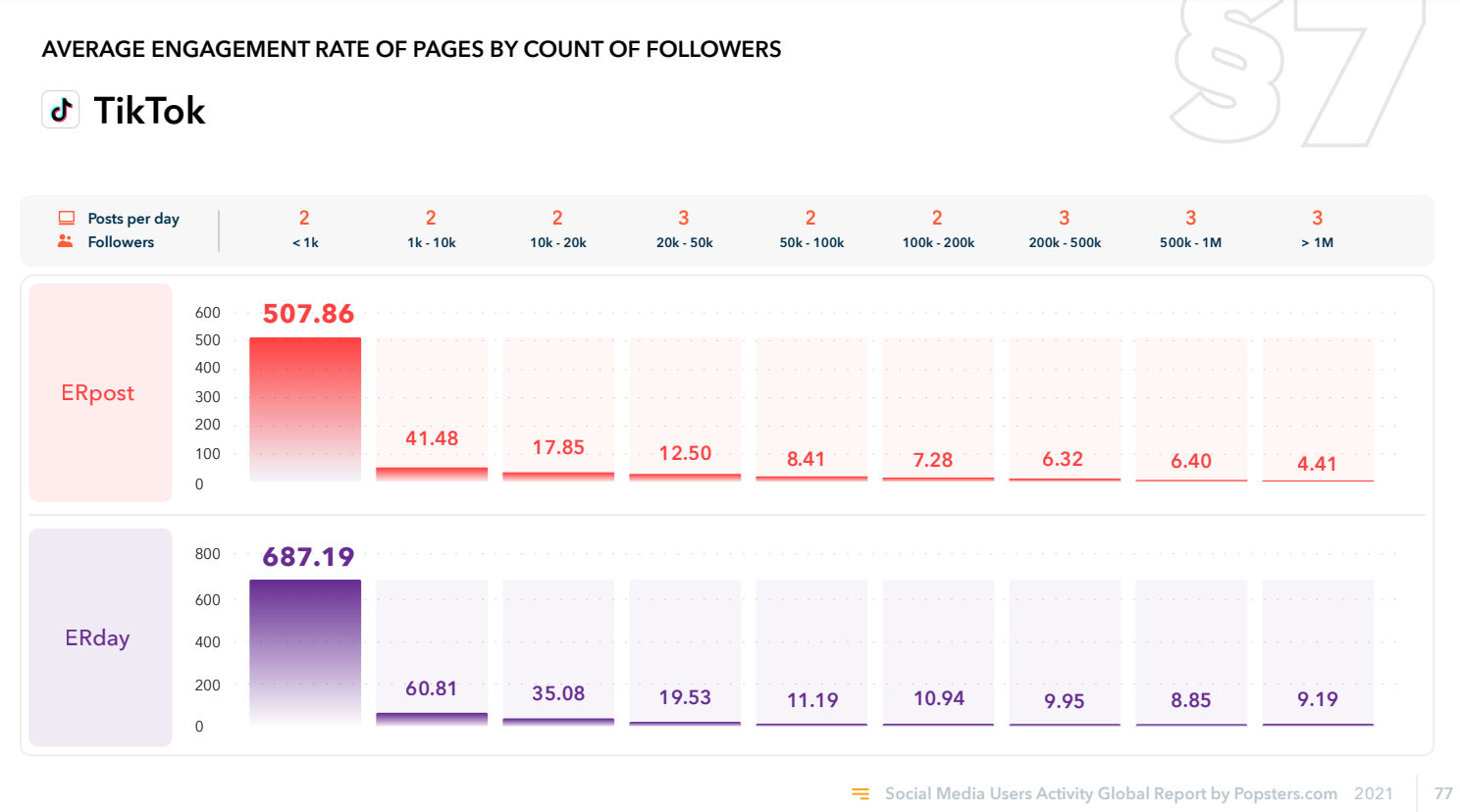
Thus, even if you have 0 followers, the video can go viral and gain millions of views - for TikTok, the main thing is the reaction of those random people to whom this video will be shown for the first time after the video is published. Because of this, TikTok has an unusually high engagement rate (ER) for small accounts. By looking at Popsters' annual research, you can see that TikTok's ER is several times higher than other social media.
Facebook recomendation system
The Facebook Algorithm is a set of rules that determine what posts people see in their Feeds. Each user's profile look different as it is personalized just for them.
The Facebook algorithm has undergone many updates and improvements over the years. One of the latest major updates is dedicated to evaluating the credibility of news articles. The purpose of this update was to prevent a person from coming across fake information.
How the Feed algorythm works
• Signals
The algorithm evaluates the relevance of each piece of content based on thousands of signals. This includes signals such as who posted it and how often you interact with them. it tries to assess relevance by understanding the nature of the content and your behavior.
Who posted it
Type of content
Interactions with the post
• Inventory
Facebook also takes inventory of all the content that can be displayed on your feed. This includes messages from people you're friends with. It also includes content from Pages you follow and groups you join.
• Predictions
The algorithm uses the given data to make predictions about what you want to see. The algorithm will analyze past behavior, your favorite topics, to try to understand how likely you are to interact with a piece of content.
• Favorites
Users can select up to 30 pages to add to Favorites. Posts from these accounts will appear higher in the feed. Don't forget there's also a feature like "I don't want to see this" and "Hide post".
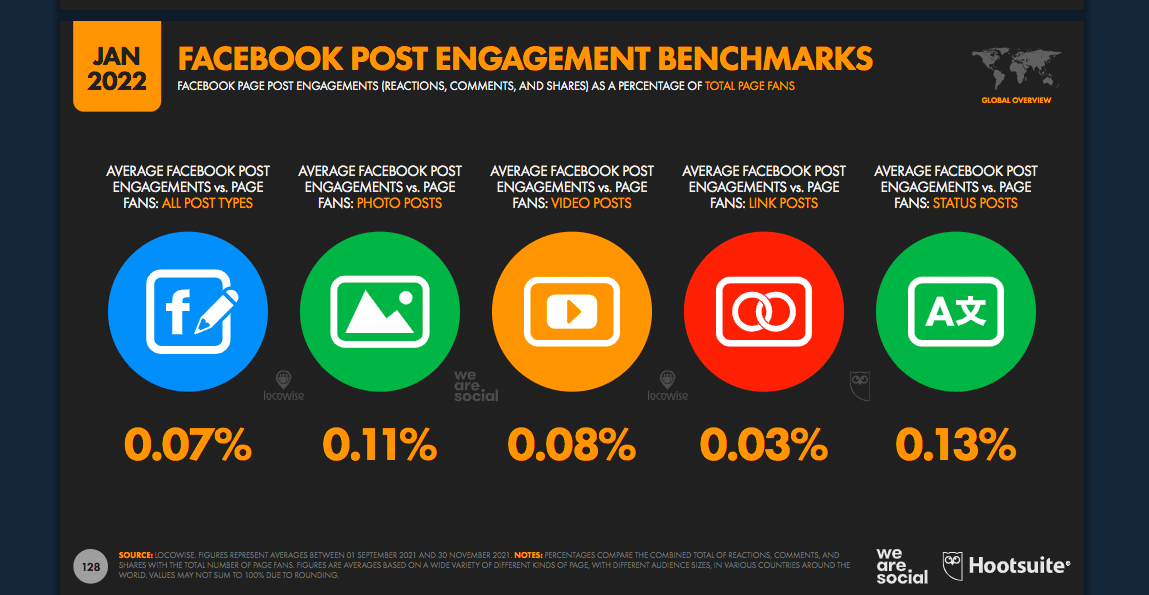
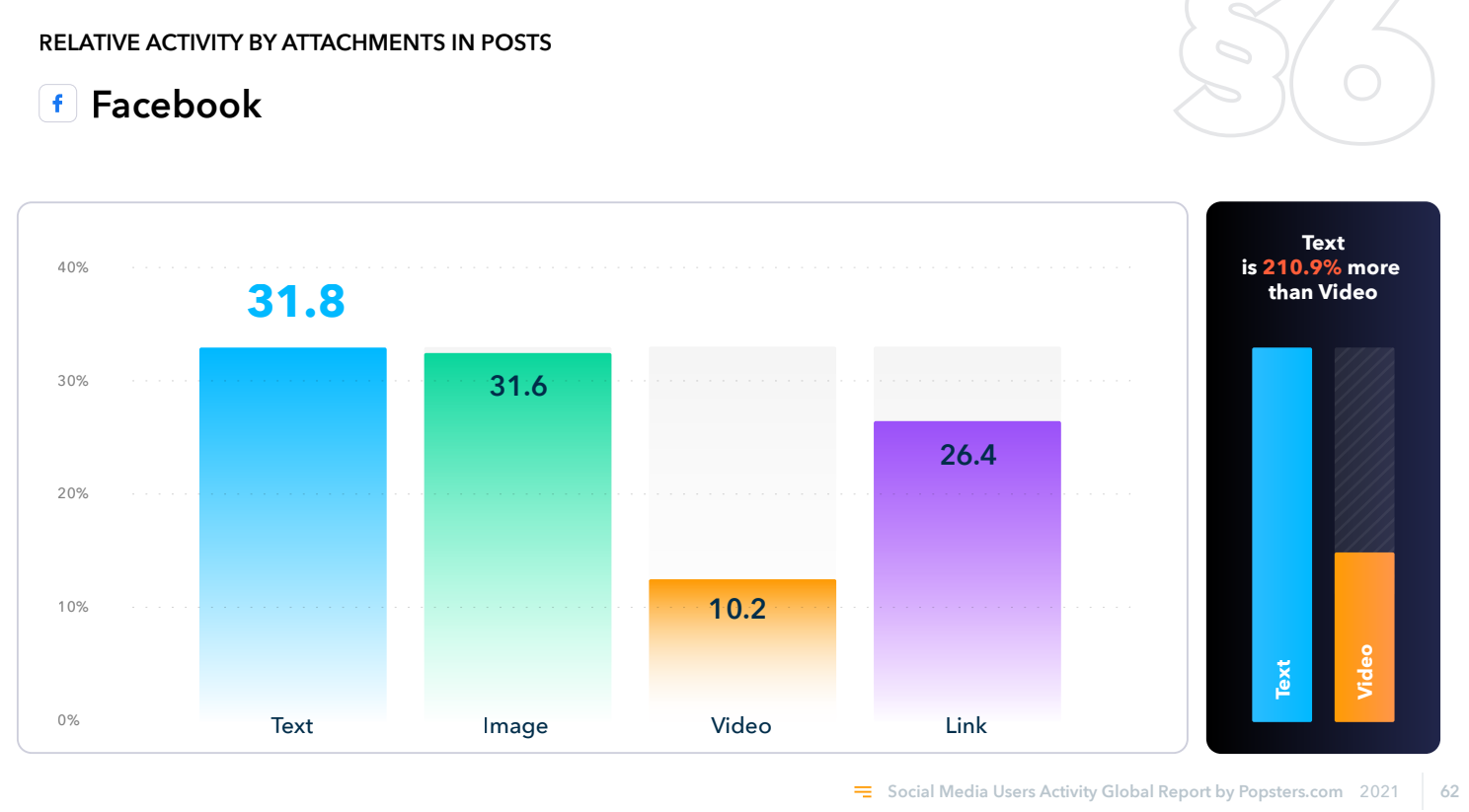
Tip: use visuals in your posts. Hootsuite’s research shows that status posts on average get the highest engagement: 0.13%. Photo posts are next at 0.11%, then videos at 0.08%, and finally link posts at 0.03%.
The Popsters also conduct an annual audience behavior research and content analysis. Posts on Facebook using text and images are the most active, followed by links and videos. The results differ, as Hootsuit used several tens of millions of posts, while Popsters used about a billion.
YouTube recommendation system
We divide YouTube recommendations into 2 conditional types:
1) Recommendations on the main page;
2) "Trending" tab.
Main page
Videos that the algorithm considers interesting for the user to get to the main page. These can be both videos from channels the user has subscribed to or interacted with recently, and channels that the user sees for the first time.
There are also recommendations that appear on the right while watching a video. Here, the algorithm considers not only interests but also similar videos to the one currently being viewed.
To select videos that are interesting to the viewer, the system considers the following factors:
- Videos that are being watched
- Videos not watched
- How much time a user spends watching a video
- Likes and Dislikes
- "Not interested" marks
- Poll results
From the Google guide:
- You don’t have to be an expert in algorithms or analytics to be successful on YouTube, instead, focus on knowing your audience. Our recommendation system doesn't promote videos to your audience but rather finds videos for your audience when they visit YouTube. Videos are ranked based on their performance and relevance to your audience.
The most important metrics considered by the algorithm for personalized recommendations are:
• Video performance - how many users with similar interests liked this video
• User's search and viewing history
Trending
Trending strives to show videos and shorts that can be interest a wide range of viewers. Basically, new clips and tracks by popular artists live here, current news being discussed, a trailer for an expected film or series, a new video by a popular author, and viral videos. Recently, Shorts videos have also been included here.
The Trending tab is personalized for each country and each language. In India, for example, the list of trending videos is different for each of the 9 common languages. YouTube updated Trending tab every 15 minutes.
To get "Trends", the video must:
• Attract a wide audience
• Don't mislead and clickbait
• Be relevant
Trending also considers:
• Number of views
• Rate of views
• Where the views come from, including third party sites
• How long ago the video was added
• How effective the video is compared to other videos on the channel
An important principle: at least half of the "Trending" videos should be from creators who regularly publish content on YouTube.
Some more facts about YouTube algorithms
1. The ranking of search results depends on the following factors:
• How well the content, title and description of the video match the query.
• How often users click on the video after the query.
2. If your video didn't get featured, but you had high hopes for it, try changing the title and icon of the video. Specifically, these actions will not affect the algorithm, but may affect the interaction of people with your video, which will already be taken into account by the algorithm.
3. For YouTube algorithms, the monetization status of the video doesn't matter.
4. Tags don't affect video discovery and it needed to read spelling errors when searching.
5. The location in the channel settings doesn't affect how often the video is shown to users from the selected region.
YouTube Shorts
A new YouTube creation and a new short video algorithm. Just note that Shorts and long videos have different algorithms, so if your Shorts are successful, this doesn't mean that the algorithm will project success on long videos.
Shorts has its own recommendations on the main page, its own feed and the ability to get into the "Trending" tab.
With Trends, the same principles apply as for long videos. Own feed focuses on interaction with videos, similar topics and common interests of users. In the recommendation's case, feed on the homepage, Shorts caters more to a broader audience (something like "Trending" for Shorts only) rather than the user's personalized feed.
We emphasize again if you have already configured the algorithm for recommending long videos for yourself, then for Shorts you will have to configure the algorithm again. For example, on YouTube you usually watch science and entertainment videos, but on Shorts you go to watch about football.
Why you shouldn't rely on algorithms
The essence of the algorithms of the recommendation system is to show users content based on their interests, regardless of the time of publication and other factors.
The scheme is simple:
Content is laid out -> content is attractive to a certain audience -> the algorithm shows content to an audience with similar interests
This is all in theory, but not everything is so simple. Popsters conducts annual social media audience research. Here are the studies for the last 3 years:
- Social Media Audience Activity Global Research 2022
- Social Media Audience Activity Global Research 2021
- Social Media Users Activity Global Research 2020
When conducting a study, we focus on the activity of interaction with publications that were published at a certain time and on a certain day of the week.
To reiterate, social media algorithms generally take into account not only interaction, but also relevance at the moment. For example, you might be shown a post three days ago. In theory, activity at different times and different days of the week should be about the same, but the numbers say otherwise. Let's look at specific statistics from the study.
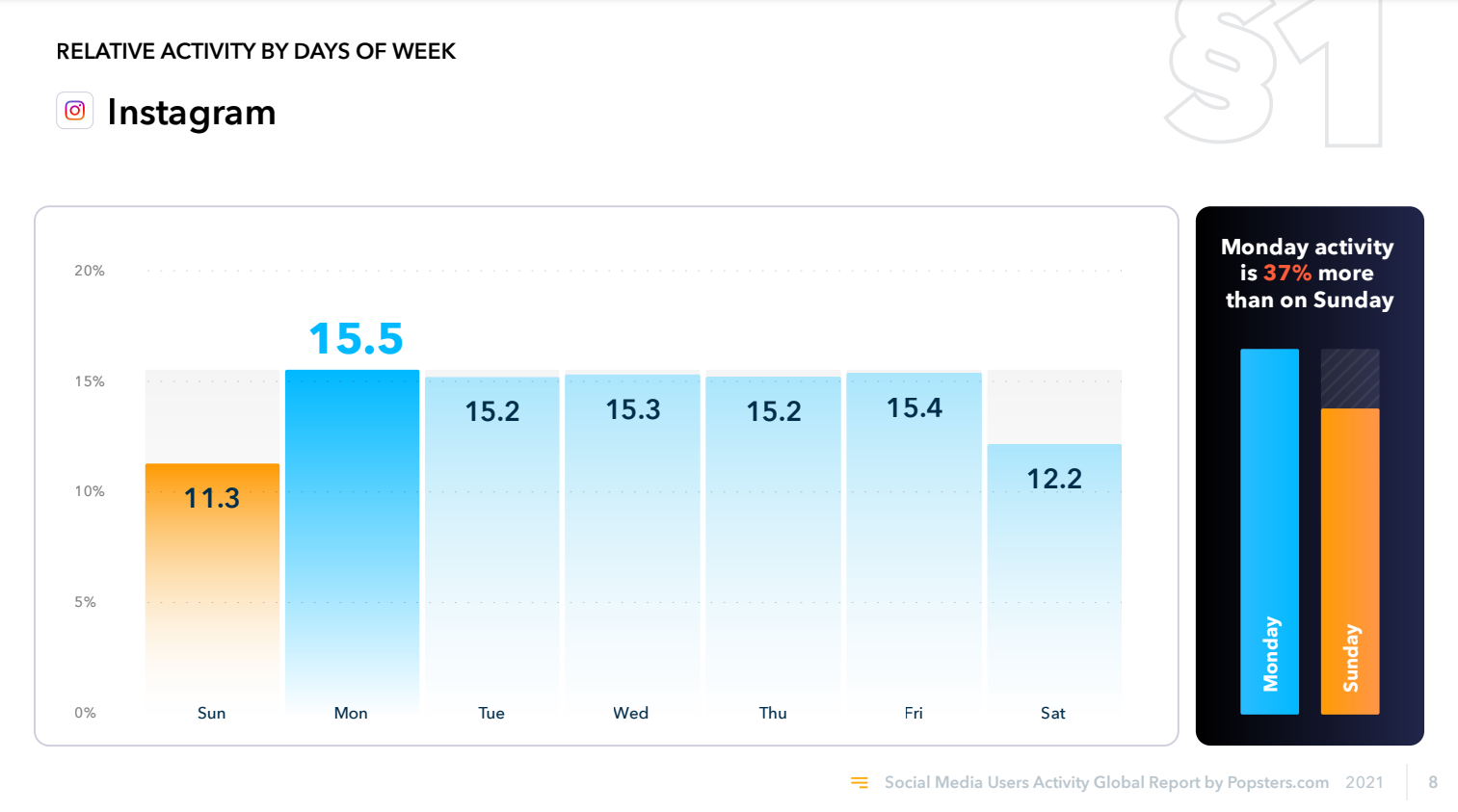
Instagram audience activity by day of the week for 2021:
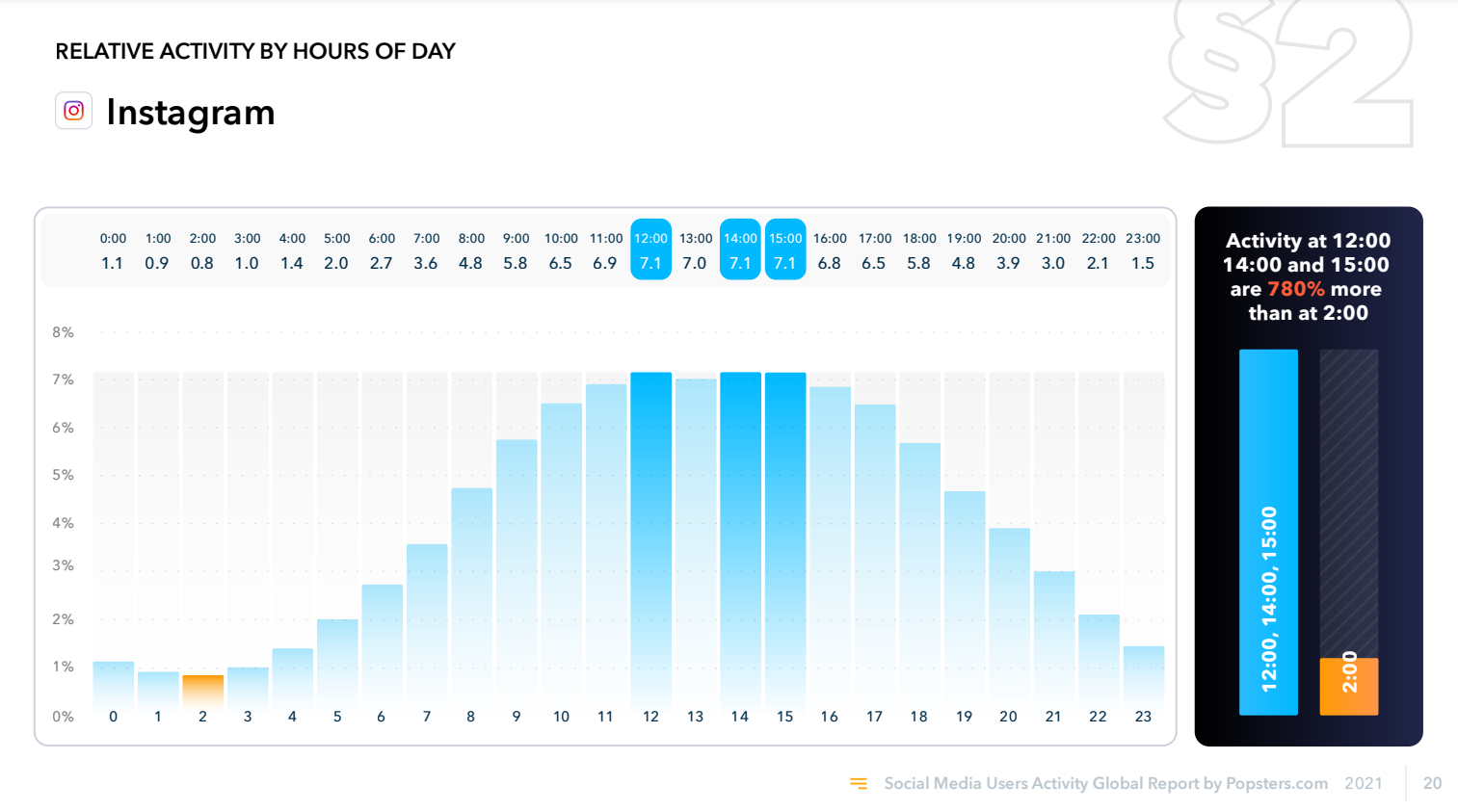
Instagram audience activity by time of day for 2021:
As you can see, the audience reacts differently to publications at different times, and this also applies to other social media. This is due to the human factor. For example, at night, people, sleepy in bed, are reluctant to interact with publications, and on Friday night they relax at parties and go to Instagram to post photos from the holiday, and not like other people's posts that appear in the feed.
In this case, we can conclude that the human factor is more important than algorithms, because modern algorithms considers only the behavior and specific actions of people, but not the emotional component.
That is why it is so important to take into account statistics and publication time along with high-quality content design.
How to ride the algorithms of any social network
Based on the foregoing, we have already concluded that algorithms should be taken into account, but not rely only on them.
In order to understand what users specifically like and what the audience interacts with more, as well as at what time it is better to post publications, deep analytics are needed. We suggest using the Popsters service.
Popsters can analyze 8 popular social networks:
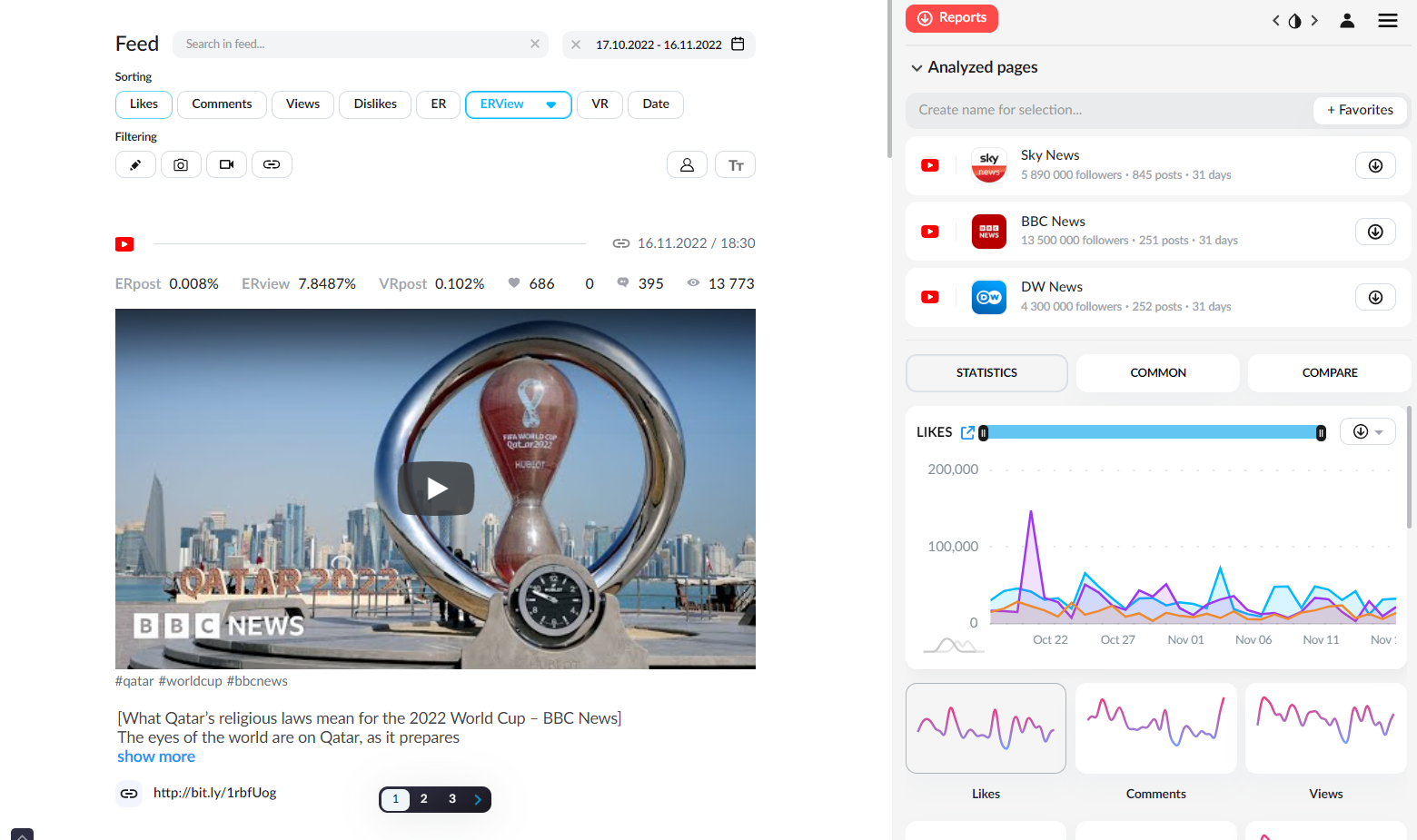
You can select several pages, including any competitors, select any period and sort publications by likes, reposts, comments, views, ER, ERView, VR, Date and other indicators.
Thus, you can track the most popular and relevant publications along with suitable conditions, get into recommendations, satisfy algorithms and consider the human factor.
Useful article on a similar topic:
- How to check Twitter analytics of any profile.
Try Popsters Trial plan to get content activity statistics of any pages for a next 7 days for free
Try for free